The Four Stages Of The Hair Growth Cycle
Hair grows in a repeating cycle made up of four stages: anagen, catagen, telogen and exogen. Each stage is crucial for maintaining hair density and overall scalp health.
- Anagen Phase: The Growth Phase
Also called the ‘active phase,’ this is when your hair is growing most rapidly. Cells at the root divide quickly to form new hair strands.
- Growth rate: Around half an inch per month (roughly six inches a year), often faster in summer.
- Duration: Typically 3-5 years, but can be longer in some individuals with up to seven years in those of Asian descent, allowing hair to grow as long as three feet.
- Age effects: The anagen phase naturally shortens with age, which can make hair growth slower and limit maximum length over time.
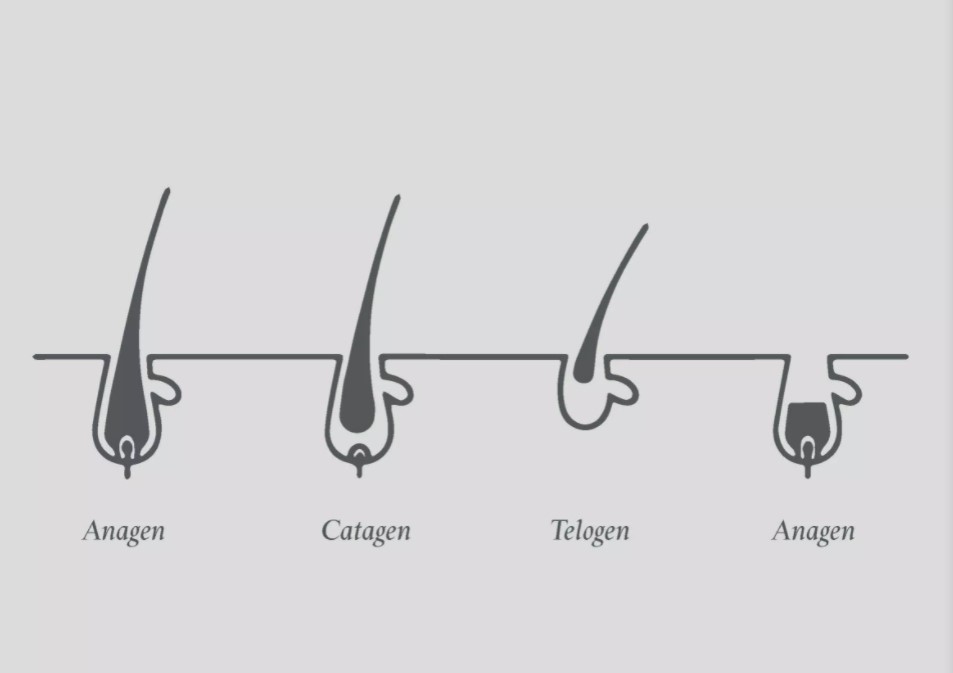
2. Catagen Phase: The Transitional Phase
This short phase signals the end of active hair growth. Individual hairs are cut off from their blood supply and cells that produce new hair.
- Proportion of hair in catagen: About 3% at any given time.
Duration: Approximately 10 days.
3. Telogen Phase: The Resting Phase
During this resting period, hairs remain in the follicle but are not actively growing.
- Proportion of hair affected by this phase: Around 10-15% at any one time.
- Duration: Approximately 100 days or three months
- Importance: Hairs stay anchored but do not lengthen, allowing the scalp to prepare for new growth.
4. Exogen Phase: The Shedding Phase
The exogen phase is when individual hairs are released from the follicle and naturally fall out. Once shedding occurs, the follicle is ready to start the cycle again with a new anagen phase.
When The Hair Growth Cycle Is Disrupted
Normally, each hair follicle works independently, which is why we all shed around 80-100 hairs a day instead of losing all of our hair at once. Disruptions to the cycle can however lead to increased hair shedding, hair thinning and slower growth or reduced hair density.
Common triggers include:
Metabolic imbalances
Illness or high fever
Nutritional deficiencies or restrictive diets
For example, telogen effluvium can occur about 12 weeks after a major stressor or illness, causing many hairs to enter the telogen phase at once. This results in noticeable hair shedding during the exogen phase. If your cycle is consistently interrupted, hair may never stay in the anagen phase long enough to reach its potential length.
Thankfully, at our Philip Kingsley Clinics, we formulate topical treatments to help follicles remain in the growth phase for as long as possible, supporting hair density and healthy growth.
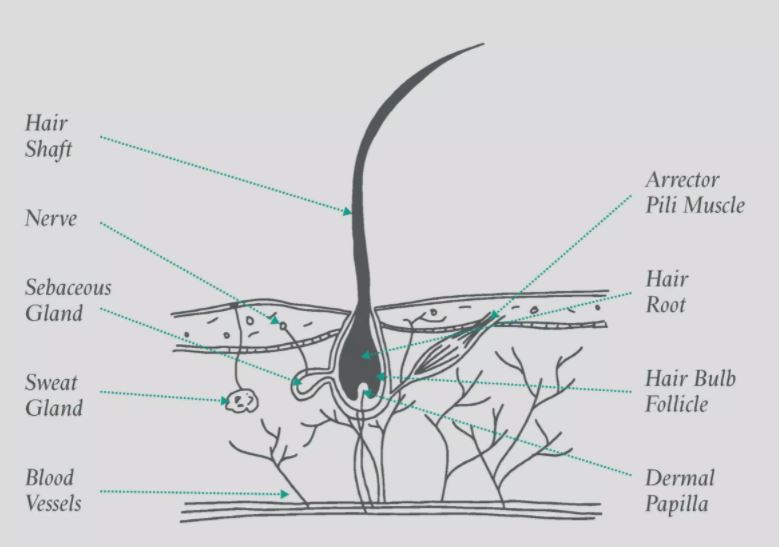
Supporting Your Hair Growth Cycle
Diet and Nutrition
Hair growth relies on a consistent intake of protein, carbohydrates and healthy fats. Nutritional supplements like our Density Amino Acid Protein Booster and Healthy Hair Complex can provide extra support to help keep your hair in optimal condition.
Minimise Stress
Stress can trigger extra hair shedding, so trying strategies to reduce and manage stress can help protect your hair. You can read more about stress and its impact on hair here.
Choose The Right Haircare Products
Using products tailored to your hair type and concerns (whether thinning, limpness or dryness) really helps your hair make the most of whichever stage of the cycle it is in.
Focus On Scalp Health
A healthy scalp is the foundation for healthy hair growth. Regular cleansing, gentle exfoliation, and targeted scalp treatments can remove buildup, promote circulation and support follicles in maintaining an optimal growth cycle. Discover our complete collection of scalp care treatments here.
Effects Of Age On The Hair Growth Cycles
As we get older, several natural changes can affect the hair cycle:
Shortening of the anagen phase, limiting maximum hair length.
Thinning and decreased density as more hairs enter the telogen phase.
Slower overall hair growth
Changes in texture or strength due to reduced follicle activity
Understanding these changes can help you adjust your haircare routine and expectations, as well as explore treatments to maintain fuller, stronger hair.
Seeking Professional Support And Advice
If you’re concerned about hair loss, thinning or slow growth, our expert Trichologists at our Philip Kingsley Clinics can provide expert diagnosis and personalised treatments as well as:
- Topical treatments to extend the growth (anagen) phase
- Nutritional guidance and supplement support
- Scalp treatments to promote follicle health
You can book a consultation here.
Your Hair Growth Cycle Questions, Answered
Q: What factors can influence the duration of each phase of the hair growth cycle?
A: The length of each phase can be affected by genetics, age, hormones, stress and seasonal changes. Hair often grows faster in summer than in winter. Nutrition and overall health also play a key role.
Q: Are there any vitamins or supplements that can support healthy hair growth and the hair growth cycle?
A: Yes. Supplements containing amino acids, protein, biotin, zinc and other nutrients can support follicle function and keep hair in the growth (anagen) phase longer. Products like our Density Amino Acid Protein Booster and Healthy Hair Complex are great for giving additional support.
Q: How to distinguish between normal and excessive shedding?
A: Shedding 80-100 hairs a day is completely normal. Excessive shedding occurs when you notice more hair falling out daily, wider partings or thinning density, which may signal a disrupted hair growth cycle.
Q: What are some common misconceptions about the hair growth cycle and hair loss?
A: Many people think hair loss means that all of your hair is falling out at once, or that hair grows continuously at the same rate. In reality, each follicle cycles independently, and shedding is natural. Hair loss or thinning often results from disrupted growth cycles.









